In questo articolo, le prime quattro tabelle che sintetizzano le forme verbali in inglese. Forma, uso e caratteristiche specifiche.
| PRESENT SIMPLE | Rappresenta il presente abituale |
| FORMA | |
| AFFERMATIVA | soggetto I/you/we/they + verbo forma base soggetto he/she/it + verbo base + -s* |
| NEGATIVA | I/you/we/they + don’t + forma base del verbo he/she/it + doesn’t + forma base del verbo |
| INTERROGATIVA | do + soggetto I/you/we/they + verbo forma base? does + soggetto he/she/it + verbo forma base? |
| RISPOSTA BREVE | Yes, I/you/we/they do – Yes, he/she/it does No, I/you/we/they don’t – No, he/she/it doesn’t |
| USO | |
| CON VERBI DI AZIONE | – azioni abituali (frasi spesso accompagnate da espressioni temporali o avverbi di frequenza come: in the morning, at night, usually, never, sometimes, seldom, often, always, rarely… = He usually wakes up at 9 o’clock – fatti e situazioni sempre vere = I come from Italy |
| CON VERBI DI STATO | – con verbi che esprimono stati mentali (think, believe, remember, know) = I think you are right – con verbi che esprimono emozioni, volontà del presente o sempre veri, percezione involontaria (love, hate, wish,like, see) = He loves music – con funzione di presente narrativo = The police arrest rioters in Trafalgar Square |
| *REGOLE 3a PERSONA | nella maggior parte dei verbi si forma aggiungendo la + -s (to work > works) |
| nei verbi terminanti in -ss, sh, -ch, -x, -o si aggiunge + -es (to watch > watches) | |
| verbi terminanti in -y preceduta da consonante = cade la y e si aggiunge + -ies (to study > studies) | |
| verbi terminanti in -y preceduta da vocale = + -s (to play >plays) |
| PRESENT CONTINUOUS | presente progressivo |
| FORMA | |
| AFFERMATIVA | soggetto + am/is/are (‘m/’s/’re)+ verbo forma -ing |
| NEGATIVA | soggetto + am/is/are + not (‘m not/isn’t/aren’t) + verbo nella forma -ing |
| INTERROGATIVA | am/is/are + soggetto + verbo nella forma -ing…? |
| RISPOSTA BREVE | Yes, soggetto + am/is/are No, soggetto+ ‘m not/ isn’t/ aren’t |
| USO | |
| VERBI DI AZIONE | – azioni in corso nel momento in cui si parla. Si utilizzano espressioni come: at present, now, at this moment = He is watching TV now – azioni in corso nel periodo in cui si parla. Si utilizzano espressioni come: in this period, these day, this week = He is living in New York in this period – azioni programmate o già stabilite che avverranno nel futuro. Si utilizzano espressioni come: tomorrow, next week, in few days = I’m coming back tomorrow |
| NOTA | Il present continuous generalmente si usa con i verbi di azione, tuttavia, ci sono casi in cui i verbi di stato e di percezione possono essere utilizzati come verbi di azione, acquisendo però un altro significato come ad esempio il verbo to have presente nelle espressioni idiomatiche, in questi casi è consentito il present continuous = I’m having a shower |
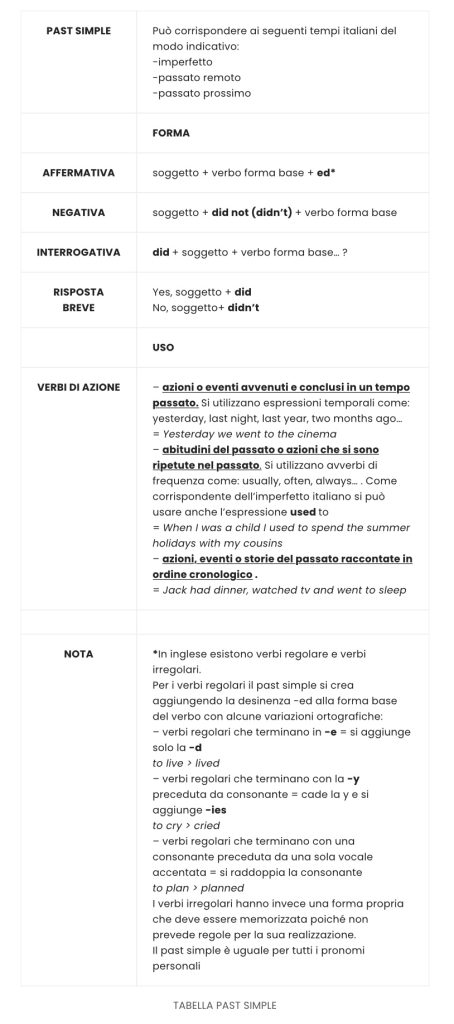
| PAST SIMPLE | Può corrispondere ai seguenti tempi italiani del modo indicativo: -imperfetto -passato remoto -passato prossimo |
| FORMA | |
| AFFERMATIVA | soggetto + verbo forma base + ed* |
| NEGATIVA | soggetto + did not (didn’t) + verbo forma base |
| INTERROGATIVA | did + soggetto + verbo forma base… ? |
| RISPOSTA BREVE | Yes, soggetto + did No, soggetto+ didn’t |
| USO | |
| VERBI DI AZIONE | – azioni o eventi avvenuti e conclusi in un tempo passato. Si utilizzano espressioni temporali come: yesterday, last night, last year, two months ago… = Yesterday we went to the cinema – abitudini del passato o azioni che si sono ripetute nel passato. Si utilizzano avverbi di frequenza come: usually, often, always… . Come corrispondente dell’imperfetto italiano si può usare anche l’espressione used to = When I was a child I used to spend the summer holidays with my cousins – azioni, eventi o storie del passato raccontate in ordine cronologico . = Jack had dinner, watched tv and went to sleep |
| NOTA | *In inglese esistono verbi regolare e verbi irregolari. Per i verbi regolari il past simple si crea aggiungendo la desinenza -ed alla forma base del verbo con alcune variazioni ortografiche: – verbi regolari che terminano in -e = si aggiunge solo la -d to live > lived – verbi regolari che terminano con la -y preceduta da consonante = cade la y e si aggiunge -ies to cry > cried – verbi regolari che terminano con una consonante preceduta da una sola vocale accentata = si raddoppia la consonante to plan > planned I verbi irregolari hanno invece una forma propria che deve essere memorizzata poiché non prevede regole per la sua realizzazione. Il past simple è uguale per tutti i pronomi personali |
| PAST CONTINUOUS | passato progressivo |
| FORMA | |
| AFFERMATIVA | soggetto + was/were + verbo forma -ing |
| NEGATIVA | soggetto + was/were not (wasn’t/weren’t) + verbo forma -ing |
| INTERROGATIVA | was/were+ soggetto + verbo forma –ing… ? |
| RISPOSTA BREVE | Yes, soggetto + was/were No, soggetto+ wasn’t/weren’t |
| USO | |
| VERBI DI AZIONE | – un’azione in corso in un momento passato = At that time he was having dinner. – azioni in corso in un momento del passato che viene interrotta da un’altra azione più breve = Yesterday I was watching Tv when someone knocked on the door – due azioni che si stavano svolgendo contemporaneamente nel passato. = Sarah was singing and Paul was playing the guitar – descrivere una situazione o ambientare la scena di un racconto nel passato = It was raining, people were running to seek shelter |